Colorize glow:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower that the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point in with a simple two- color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
 |
 |
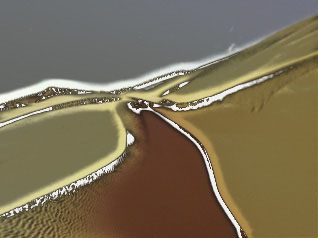 |
| Black Point= -75 | Black Point=0 | Black Point=75 |
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Decreasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
The illustrations below show the affect of adjusting the White Point in with a simple two- color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
 |
 |
 |
| White Point=100 | White Point=50 | White Point=25 |
Negative Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
 |
 |
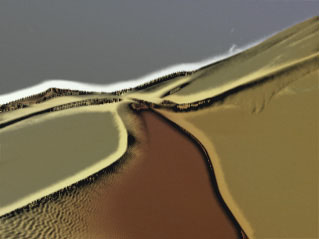 |
| Squeeze= -75 | Squeeze=0 | Squeeze=75 |
**Advanced Gradient Controls Parameter Group:**The Advanced Gradient Controls parameter group is located inside the Colorize parameter group.
The Loop Mode menu affects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
Forward Loop is the most useful choice and is the default value. When you choose Forward Loop, increase Loop Count to create a gradient that loops back toColor 1 after it passes Color 6. Change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
When you use Forward Loop, increaseCrossfade End Colors to a value other than 0 so that the final image does not appear to jump.
When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc. An advantage to this choice is that your final image will not jump.
When Off is chosen, going past the end of the gradient will use the end color.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient, and negative values loop backwards, which will only have a different appearance from a positive value if Gradient Offset is not set to 0. Set Crossfade End Colors to a value other than zero when you use Loop Count. This will prevent the rendered image from jumping.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient. Set Crossfade End Colors to a value other than zero when you use Gradient Offset. This will prevent the rendered image from jumping.
Color Ease adjusts the softness of the transitions between pure colors in the gradient. Increasing positive values cause the transitions to be more abrupt. Decreasing negative values soften the transitions.
 |
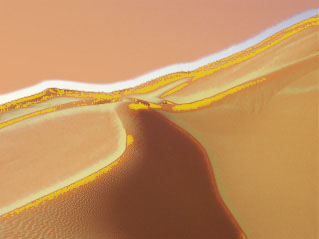 |
| Color Ease= -100 | Color Ease=100 |
**Gradient HSL Parameter Group:**The Gradient HSL parameter group is located inside the Colorize parameter group.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
Lightness controls the brightness of the colors in the gradient. Higher values lighten the colors, while lower values darken the colors.
Light Zoom
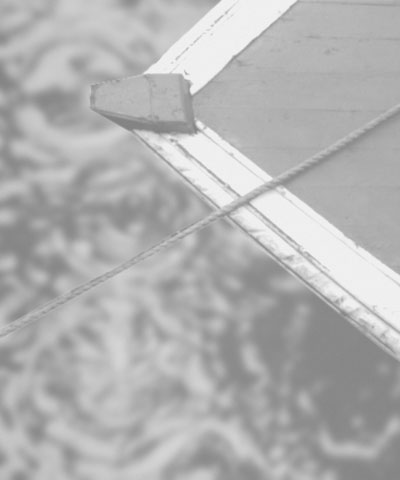
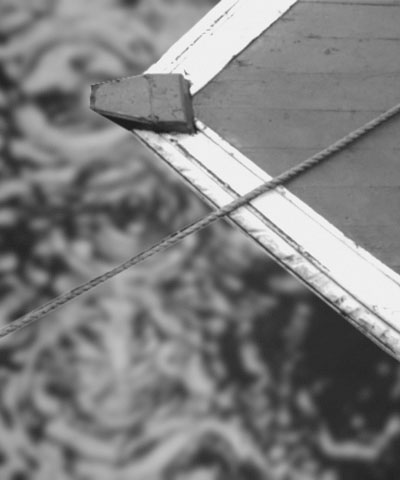
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower that the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point in with a simple two- color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
 |
 |
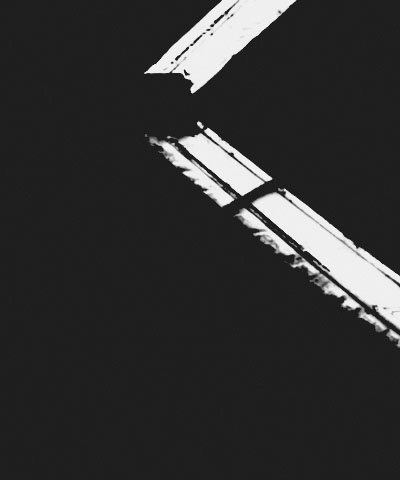 |
| Black Point= -75 | Black Point=0 | Black Point=75 |
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Decreasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the White Point in with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
 |
 |
 |
| White Point=100 | White Point=50 | White Point=25 |
Negative Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
 |
 |
 |
| Squeeze= -75 | Squeeze=0 | Squeeze=75 |
TheLoop menuaffects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Offis chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you choose Forward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color 6. You can increaseLoop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you chooseBack & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value if Gradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Color Ease adjusts the softness of the transitions between pure colors in the gradient. Increasing positive values causes the transitions to be more abrupt. Decreasing negative values softens the transitions.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
Lightness controls the brightness of the colors in the gradient. Higher values lighten the colors, while lower values darken the colors.
Rays Cartoon:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
The Loop Modeaffects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you chooseForward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color**6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value ifGradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
rays dissolve:
Black Point: Adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
 |
 |
 |
| Black Point= -75 | Black Point=0 | Black Point=75 |
White Point: Adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
**Squeeze:**Negative values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
 |
 |
 |
| Squeeze= -75 | Squeeze=0 | Squeeze=75 |
Huecycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
Rays puffy
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
 |
 |
 |
| Black Point= -75 | Black Point=0 | Black Point=75 |
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Negative Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
 |
 |
 |
| Squeeze= -75 | Squeeze=0 | Squeeze=75 |
The Loop Modeaffects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you choose Forward Loop the gradient loops back toColor 1 after it passes Color 6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Countsets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value if Gradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Huecycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
Rays Radiant Edges:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
The Loop Modeaffects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you chooseForward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color**6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value ifGradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
Rays Radiant Spotlight:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Negative Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
The Loop menu affects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you chooseForward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color**6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value ifGradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
Rays Ring:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
The Loop Modeaffects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you chooseForward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color**6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value ifGradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
rays ripply:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
The Loop modeaffects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you chooseForward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color**6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value ifGradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
rays streaky:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
The Loop modeaffects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you chooseForward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color**6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value ifGradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
rays textured:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
The Loop modeaffects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you chooseForward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color**6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value ifGradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
Rays wedge:
Black Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is treated as the pure Color 1 level in the output. All pixels whose Input Channel value is lower than the Black Point value are mapped to the Color 1 color. Increasing positive Black Point values cause more pixels to be purely Color 1 in the output. Decreasing negative values cause fewer pixels to be purely Color 1. The following illustrations show the affect of adjusting the Black Point with a simple two-color gradient from black (Color 1) to white (Color 6).
White Point adjusts the value in the Input Channel which is mapped to the pure Color 6 in the output. Increasing White Point causes more pixels to be purely Color 6 in the output.
Squeeze values compress and shift the gradient towards the left (Color 1) side. Increasing positive values compress and shift the gradient towards the right (Color 6) side.
The Loop Mode affects the output when either Loop Count or Gradient Offset are changed from their default values.
- When Off is chosen, looping past the end of the gradient uses the end color. This is the default value.
- When you chooseForward Loop the gradient loops back to Color 1 after it passes Color**6. You can increase Loop Count to set the number of loops or change Gradient Offset to move the mapping through this loop.
- When you choose Back & Forth Loop, the color mapping goes from 1 to 6 to 6 to 1, etc.
Loop Count sets the number of times that the gradient loops. Values less than one use less of the gradient; negative values loop backwards, which only has a different appearance from a positive value ifGradient Offset is not zero.
Gradient Offset offsets the starting point of the gradient. This can be animated to create palette-shifting effects. A value of 100 offsets the gradient by one full cycle. Since the gradient loops back and forth, setting Gradient Offset to 100 or 300 simply reverses the direction of the gradient.
Hue cycles the colors in the gradient around the color wheel in the HSL color space.
Saturation adjusts the intensity of each color’s hue in the gradient. Negative values desaturate the gradient, while positive values increase the saturation of the gradient.
